AIMs: Explain the drawbacks to using a DV01-neutral hedge for a bond position. Describe a regression hedge and explain how it improves on a standard DV01-neutral hedge. Calculate the regression hedge adjustment factor, beta. Calculate the face value of an offsetting position needed to carry out a regression hedge.
Questions:
321.1. A trader shorts $100.0 million of nominal US Treasury 3 5/8s bonds and, in a relative trade, wants to hedge with a long in US Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (TIPS); the relative trade will express a view on inflation as reflected in the spread between the rate of the nominal bond and a TIPS. The yields and DV01s of each bond are shown below, in addition to the output from a regression of nominal yield changes against real (TIPS) yield changes:
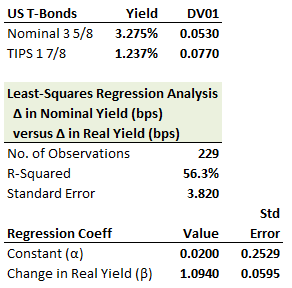
Which is nearest to the face amount of the long position in the 1 7/8s TIPS needed to carry out a regression hedge?
a. $6.8 million face amount of TIPS
b. $68.83 million face amount of TIPS
c. $75.30 million face amount of TIPS
d. $105.68 million face amount of TIPS
321.2. A trader shorts $100.0 million of nominal US Treasury 3 5/8s bonds and, employing a single-variable regression hedge, buys a face amount of 1 7/8s US TIPS. The bonds are show below in addition to the results of a regression of the nominal against real yield:
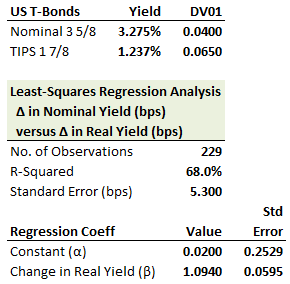
Which is nearest to an estimate of the daily volatility of the P&L of the hedged portfolio?
a. $2,380
b. $43,760
c. $67,323
d. $212,000
321.3. A trader shorts $100.0 million of nominal US Treasury 3 5/8s bonds and hedges with a purchase of a face amount of 1 7/8s US TIPS based on the regression results of a single-variable hedge, which are shown here:
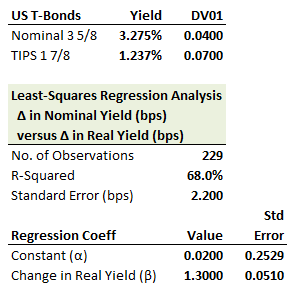
Each of the following are true about this regression hedge EXCEPT for which is false?
a. The regression model estimates a correlation between changes in the nominal and real yields of about 82.5%
b. We can be 95% confident that the true value of beta is unity (1.0)
c. The daily volatility of the P&L of the hedged portfolio is about $88,000
d. The difference between a DV01-hedge and a regression hedge is about $17.14 million face amount of the TIPS
Answers:
Questions:
321.1. A trader shorts $100.0 million of nominal US Treasury 3 5/8s bonds and, in a relative trade, wants to hedge with a long in US Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (TIPS); the relative trade will express a view on inflation as reflected in the spread between the rate of the nominal bond and a TIPS. The yields and DV01s of each bond are shown below, in addition to the output from a regression of nominal yield changes against real (TIPS) yield changes:

Which is nearest to the face amount of the long position in the 1 7/8s TIPS needed to carry out a regression hedge?
a. $6.8 million face amount of TIPS
b. $68.83 million face amount of TIPS
c. $75.30 million face amount of TIPS
d. $105.68 million face amount of TIPS
321.2. A trader shorts $100.0 million of nominal US Treasury 3 5/8s bonds and, employing a single-variable regression hedge, buys a face amount of 1 7/8s US TIPS. The bonds are show below in addition to the results of a regression of the nominal against real yield:

Which is nearest to an estimate of the daily volatility of the P&L of the hedged portfolio?
a. $2,380
b. $43,760
c. $67,323
d. $212,000
321.3. A trader shorts $100.0 million of nominal US Treasury 3 5/8s bonds and hedges with a purchase of a face amount of 1 7/8s US TIPS based on the regression results of a single-variable hedge, which are shown here:

Each of the following are true about this regression hedge EXCEPT for which is false?
a. The regression model estimates a correlation between changes in the nominal and real yields of about 82.5%
b. We can be 95% confident that the true value of beta is unity (1.0)
c. The daily volatility of the P&L of the hedged portfolio is about $88,000
d. The difference between a DV01-hedge and a regression hedge is about $17.14 million face amount of the TIPS
Answers:
