AIMs: Calculate VaR using the historical simulation and hybrid approaches on the same data set. Summarize the study results using the various VaR measurement approaches.
Questions:
401.1. The following table displays the six worst returns over the previous 100 days (K = 100) and the weights assigned to each return under the hybrid (EXP), with lambda = 0.940, and simple historical simulation (HS) approaches:
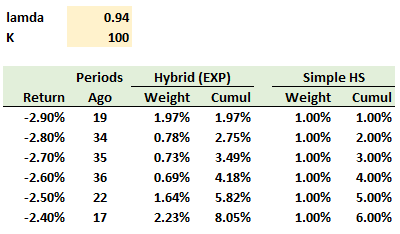
If we assume (per the Boudoukh reading) that "1/2 of a given return’s weight is to the right and 1/2 to the left of the actual observation" and "the required VaR level is a linearly interpolated return, where the distance to the two adjacent cumulative weights determines the return," which returns are nearest to the 95.0% value at risk (VaR) under, respectively, the hybrid and simple HS approaches?
a. 2.45% (hybrid) and 2.50% (HS)
b. 2.50% (hybrid) and 2.45% (HS)
c. 2.55% (hybrid) and 2.55% (HS)
d. 2.60% (hybrid) and 2.60% (HS)
401.2. The following table displays the seven worst returns over the previous one hundred days (K = 100) and the weights assigned to each return under the hybrid (EXP), with lambda = 0.970, and simple historical simulation (HS) approaches:
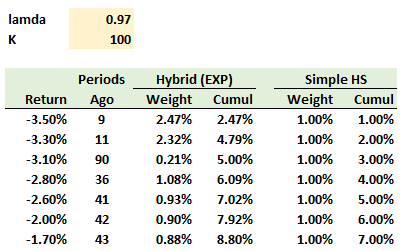
Which returns are nearest to the 95.0% value at risk (VaR) under, respectively, the hybrid and simple HS approaches?
a. 2.95% (hybrid) and 2.30% (HS)
b. 3.10% (hybrid) and 2.00% (HS)
c. 3.10% (hybrid) and 2.60% (HS)
d. 3.30% (hybrid) and 2.80% (HS)
401.3. The Boudoukh reading says, "The adaptability of a VaR method is one of the most critical elements in determining the best way to measure VaR. When a large return is observed, the VaR level should increase. It should increase, however, in such a way which will make the next tail event’s probability precisely x%. We can therefore expect these tail event realizations to be i.i.d. events with x% probability. This i.i.d.-ness can be examined using the autocorrelation of these tail events, with the null being that it is zero." Which of the following statements best summarizes the results of the corresponding statistical test?
a. The HYBRID approach outperformed EXP and HS with generally lower autocorrelations and higher p-values for independence
b. The HYBRID approach outperformed EXP and HS with generally higher autocorrelations and lower p-values for independence
c. The HS approach, with higher autocorrelations, generally outperformed the HYBRID approach which generally outperformed the EXP approach
d. The EXP approach, with lower p-values for independence, generally outperformed the HYBRID approach which generally outperformed the HS approach
Answers here:
Questions:
401.1. The following table displays the six worst returns over the previous 100 days (K = 100) and the weights assigned to each return under the hybrid (EXP), with lambda = 0.940, and simple historical simulation (HS) approaches:

If we assume (per the Boudoukh reading) that "1/2 of a given return’s weight is to the right and 1/2 to the left of the actual observation" and "the required VaR level is a linearly interpolated return, where the distance to the two adjacent cumulative weights determines the return," which returns are nearest to the 95.0% value at risk (VaR) under, respectively, the hybrid and simple HS approaches?
a. 2.45% (hybrid) and 2.50% (HS)
b. 2.50% (hybrid) and 2.45% (HS)
c. 2.55% (hybrid) and 2.55% (HS)
d. 2.60% (hybrid) and 2.60% (HS)
401.2. The following table displays the seven worst returns over the previous one hundred days (K = 100) and the weights assigned to each return under the hybrid (EXP), with lambda = 0.970, and simple historical simulation (HS) approaches:

Which returns are nearest to the 95.0% value at risk (VaR) under, respectively, the hybrid and simple HS approaches?
a. 2.95% (hybrid) and 2.30% (HS)
b. 3.10% (hybrid) and 2.00% (HS)
c. 3.10% (hybrid) and 2.60% (HS)
d. 3.30% (hybrid) and 2.80% (HS)
401.3. The Boudoukh reading says, "The adaptability of a VaR method is one of the most critical elements in determining the best way to measure VaR. When a large return is observed, the VaR level should increase. It should increase, however, in such a way which will make the next tail event’s probability precisely x%. We can therefore expect these tail event realizations to be i.i.d. events with x% probability. This i.i.d.-ness can be examined using the autocorrelation of these tail events, with the null being that it is zero." Which of the following statements best summarizes the results of the corresponding statistical test?
a. The HYBRID approach outperformed EXP and HS with generally lower autocorrelations and higher p-values for independence
b. The HYBRID approach outperformed EXP and HS with generally higher autocorrelations and lower p-values for independence
c. The HS approach, with higher autocorrelations, generally outperformed the HYBRID approach which generally outperformed the EXP approach
d. The EXP approach, with lower p-values for independence, generally outperformed the HYBRID approach which generally outperformed the HS approach
Answers here:
